Imagine spending your Monday morning manually renaming 500 files, copying data between spreadsheets, and sending the same email to 50 different clients. Now imagine clicking one button and watching all of that happen in 30 seconds. That's the power of Python automation — and it's more accessible than most people realize.
According to a McKinsey study, knowledge workers spend up to 28% of their workweek managing emails and nearly 20% searching for information. Python automation eliminates these time sinks by handling repetitive tasks while you focus on work that actually requires human creativity and decision-making.
What Makes Python the Go-To Language for Automation
Python dominates the automation landscape for three compelling reasons. First, its syntax reads almost like plain English — even someone who has never written code can understand what a Python script does. Second, Python's ecosystem includes thousands of specialized libraries designed specifically for automation tasks. Third, it runs on Windows, Mac, and Linux without modification.
Unlike complex enterprise automation tools that require expensive licenses and months of training, Python is completely free and can be learned in weeks. The barrier to entry has never been lower, especially with AI-powered coding assistants that can help write and debug scripts in real-time.
5 Automation Scripts That Deliver Immediate Results
The most impactful automation scripts aren't necessarily the most complex. Here are five scripts that consistently save professionals hours every week:
1. Intelligent File Organization
This script monitors your Downloads folder and automatically sorts files into appropriate directories based on file type, date, or custom naming patterns. What used to take 15 minutes of daily manual sorting now happens instantly in the background.
import os
import shutil
from pathlib import Path
downloads = Path.home() / "Downloads"
destinations = {
".pdf": "Documents/PDFs",
".jpg": "Pictures",
".xlsx": "Documents/Spreadsheets"
}
for file in downloads.iterdir():
if file.suffix in destinations:
dest = Path.home() / destinations[file.suffix]
dest.mkdir(exist_ok=True)
shutil.move(str(file), str(dest / file.name))
2. Automated Report Generation
Pulling data from multiple sources and compiling reports manually is tedious and error-prone. A Python script using pandas can aggregate data from CSV files, databases, and APIs, then generate formatted reports automatically every morning before you even start work.
3. Email Automation with Smart Filtering
Rather than manually sending identical updates to multiple stakeholders, Python scripts can personalize and send emails based on recipient data, track responses, and even follow up automatically when needed.
4. Web Data Collection
Whether you're monitoring competitor prices, tracking job postings, or gathering research data, web scraping scripts can collect information from hundreds of pages in minutes — a task that would take days to do manually.
5. Data Cleaning and Transformation
Raw data rarely arrives in the format you need. Python automation can standardize date formats, remove duplicates, fill missing values, and transform data structures without manual intervention.
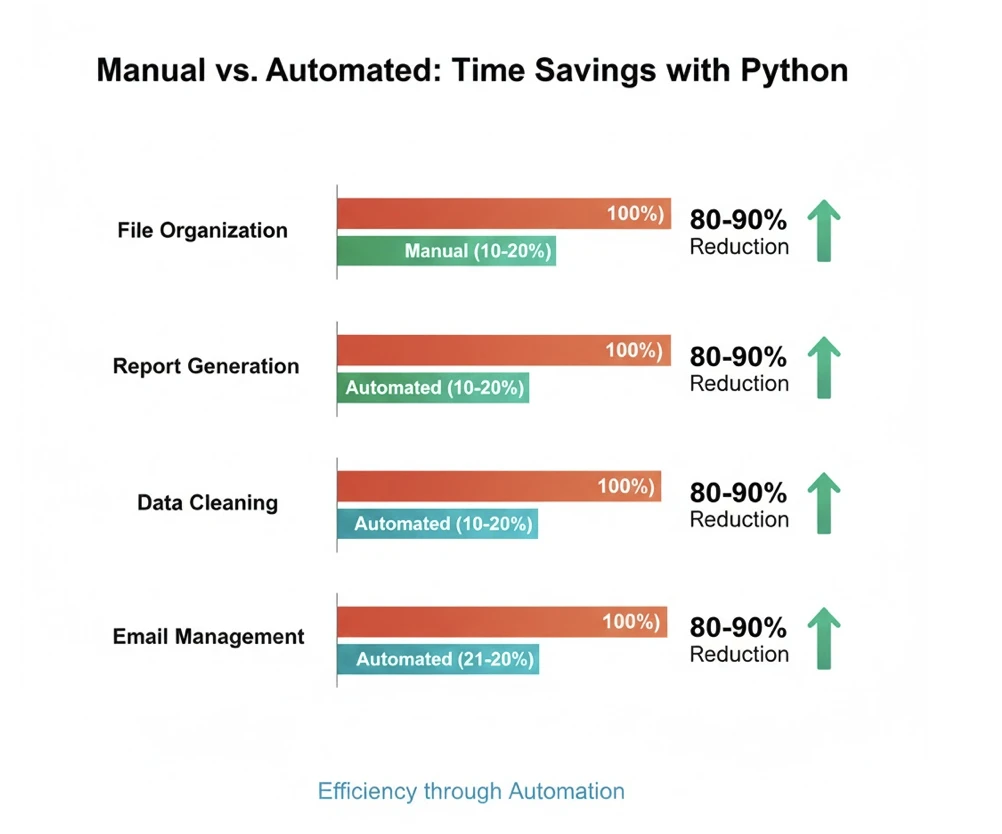
The Real Numbers: How Much Time Automation Actually Saves
Let's break down the math with real examples from professionals who implemented Python automation:
- Marketing Manager: Reduced weekly reporting time from 6 hours to 20 minutes
- Data Analyst: Cut data cleaning tasks from 8 hours to 45 minutes per dataset
- Administrative Assistant: Automated file organization saving 5 hours weekly
- Sales Representative: Email follow-up automation freed up 4 hours per week
These aren't theoretical projections — they represent documented time savings from professionals who invested a few days learning Python basics and building their first automation scripts.
Essential Python Libraries for Automation
The Python ecosystem provides specialized tools for virtually every automation need:
| Library | Use Case | Difficulty Level |
|---|---|---|
| os / shutil | File and folder operations | Beginner |
| pandas | Data manipulation and analysis | Beginner-Intermediate |
| requests | HTTP requests and API interactions | Beginner |
| BeautifulSoup | Web scraping and HTML parsing | Beginner |
| Selenium | Browser automation | Intermediate |
| PyAutoGUI | Desktop GUI automation | Beginner |
| schedule | Task scheduling | Beginner |
| smtplib | Email sending | Beginner |
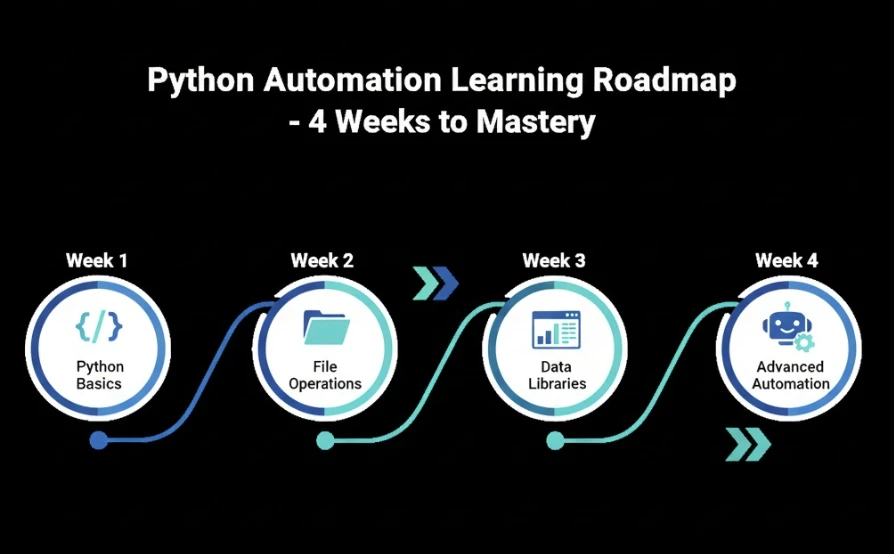
Getting Started: Your First Week of Python Automation
The path from complete beginner to productive automation user is shorter than most people expect. Here's a realistic progression:
Days 1-2: Install Python and learn basic syntax — variables, loops, and conditional statements. Focus on understanding how Python reads and executes code.
Days 3-4: Work with files and folders using the os and shutil libraries. Create your first useful script that organizes files automatically.
Days 5-7: Explore pandas for data manipulation or requests for web interactions, depending on your specific needs. Build a script that solves a real problem you face weekly.
For a structured approach with hands-on projects, the complete Python automation guide provides step-by-step tutorials covering everything from basic scripts to advanced automation workflows.
Common Automation Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Even experienced programmers make these errors when building automation scripts:
Hardcoding Sensitive Information
Never include passwords, API keys, or personal data directly in your scripts. Use environment variables or secure credential managers instead. A script shared accidentally or committed to a public repository could expose sensitive information.
Ignoring Error Handling
Automation scripts often run unattended. Without proper error handling, a script might fail silently, leaving you unaware that tasks haven't been completed. Always implement logging and notifications for script failures.
Over-Automating Too Soon
Start with simple, high-impact tasks before attempting complex workflows. A script that saves 30 minutes daily is more valuable than an ambitious project that never gets finished.
Neglecting Testing
Test automation scripts thoroughly with sample data before running them on important files. A bug in a file organization script could move or rename critical documents incorrectly.
Python Automation in 2026: AI-Enhanced Workflows
The automation landscape has evolved significantly with AI integration. Modern Python automation increasingly incorporates:
- Natural Language Processing: Scripts that understand and respond to human language for smarter email filtering and document classification
- Intelligent Decision Making: AI models that determine actions based on context rather than rigid rules
- Self-Correcting Scripts: Automation that adapts when websites change structure or data formats shift
- Voice-Activated Automation: Triggering scripts through voice commands for hands-free operation
These advancements make automation more powerful while remaining accessible to non-programmers who can describe what they want in plain English.
Building Your Automation Toolkit
Success with Python automation comes from building a personal library of reusable scripts. Start by documenting every repetitive task you perform for one week. Rate each task by frequency and time consumed. The tasks that score highest on both metrics are your best automation candidates.
Create a dedicated folder for automation scripts and maintain clear documentation for each one. As your collection grows, you'll find yourself combining smaller scripts into powerful workflows that handle entire processes automatically.

Taking the Next Step
Python automation represents one of the highest-return skills you can develop. The investment of a few weeks learning translates into hundreds of hours saved annually — time you can redirect toward strategic work, learning new skills, or simply achieving better work-life balance.
Whether you're a complete beginner or an experienced programmer looking to streamline workflows, the resources available today make getting started easier than ever. The only question is how much time you'll continue losing to manual tasks before taking action.
For those ready to begin, exploring a structured Python automation curriculum can accelerate the learning process significantly compared to piecing together information from scattered tutorials.





.jpg)


